“Did you know that a solid-state drive (SSD) can copy a 20 GB movie in less than ten seconds? In comparison, a hard disk drive (HDD) takes at least two minutes. This speed difference (SSD vs. HDD) is why SSDs are becoming more popular than HDDs.
Choosing the right data storage device is crucial in today’s digital world. Both SSDs and HDDs store and retrieve data but function very differently (SSD and HDD). SSDs use memory chips, offering fast speed and durability, while HDDs rely on spinning disks, providing more storage at a lower cost.”
Key Takeaways
- SSDs can copy files much faster than HDDs, doing the job in a short time.
- HDDs are a good choice for storing lots of data at a lower cost per GB.
- SSDs are quicker for starting up and loading apps because they read and write data fast.
- SSDs are more durable than HDDs because they don’t have moving parts and can handle shocks better.
- Choosing between SSD and HDD depends on what you need, like speed, storage, and cost.
Introduction to SSD and HDD: Basics and Key Differences
The debate between SSD and HDD often arises when looking at storage options. Each has its pros and cons. Knowing how a solid-state drive (SSD) and a hard disk drive (HDD) work is critical to choosing the proper storage for you.
SSDs use flash memory and memory chips to store data electronically. They don’t have moving parts, making them more durable and quick to access data. However, HDDs use spinning platters and a mechanical arm to read and write data. This makes them more likely to break mechanically. SSDs are faster at reading and writing data because they don’t move parts around.
The main difference between SSD and HDD performance is how fast they access data. SSDs are much faster, which means quicker startup times, faster file transfers, and a smoother system. HDDs are slower, with speeds of 80-160MB/s, compared to SSDs’ 200-550MB/s. This is because SSDs handle more tasks at once.
HDDs can store much data, up to 16TB, and are cheaper per gigabyte. But SSDs use less power, are quieter, and handle shocks better, making them great for on-the-go devices.
Choosing between an SSD and an HDD depends on what you need. SSDs are great for speed, saving energy, and being tough. HDDs offer more storage for the money. Let’s look at these differences in a detailed comparison:
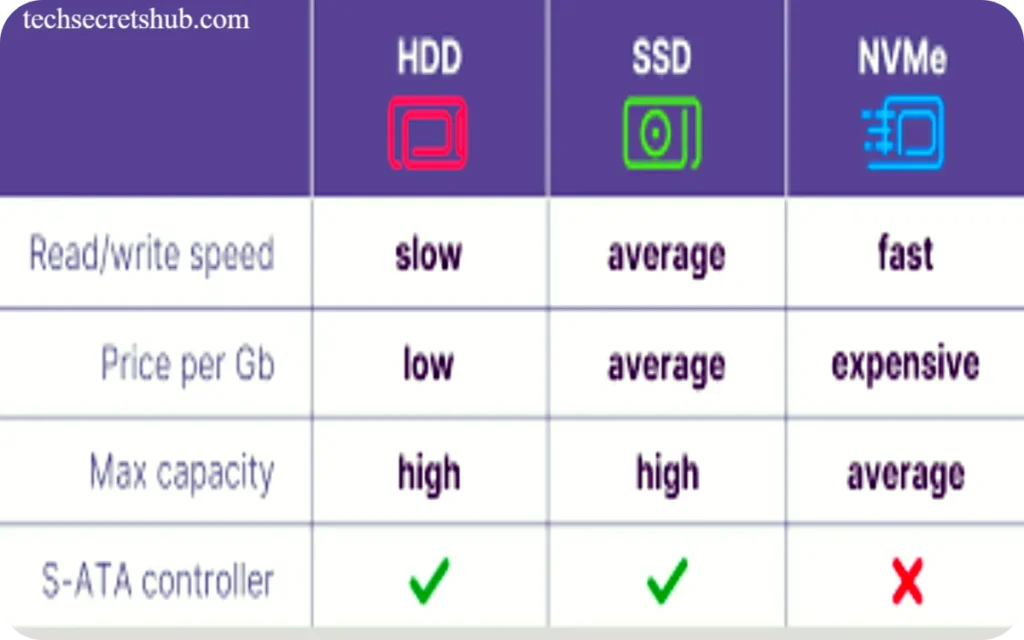
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Flash Memory | Spinning Platters |
| Speed | 200-550MB/s | 80-160MB/s |
| Durability | High | Prone to Mechanical Failure |
| Price | More Expensive | Less Expensive |
| Power Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Noise | Silent | Can Produce Noise |
| Capacity | Lower per Dollar | Higher per Dollar |
What is a Hard Disk Drive (HDD)?
An HDD, or hard disk drive, is used in computers and other digital systems. It uses magnetic storage to read and write data. By understanding its main parts and how they work, we see why HDDs are still a top choice for storing data, even with SSDs around.
How HDDs Work
At the heart of an HDD, you’ll find key parts like the platter, actuator arm, and spinning disk. These work together to store data efficiently. The platter stores data magnetically and spins fast. The actuator arm moves magnetic heads over the disk to read and write data.
Data processing in an HDD means the disk spins fast, letting magnetic heads access and change data on the platter. This movement is mechanical, which means it takes longer than SSDs. But, HDDs still have good read/write speeds, often under 250MB per second. This makes them great for many uses.
Key Features of HDDs
- Capacity: HDDs can store a lot of data, up to 22TB. They’re perfect for big storage needs.
- Cost: Even with SSD prices dropping, HDDs are still a budget-friendly choice. You can get a 2TB internal drive for just $60.
- Durability: HDDs might not be as tough as other parts, but they’ve been reliable for years.
- Versatility: HDDs fit many uses, from personal computers to big servers. They offer more storage space and are cheaper.
- Latency: HDDs take longer to access data than SSDs, but they’re still good enough for most everyday tasks and storing lots of data.
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Read/Write Speeds | Up to 250MB/s | Up to 7,000MB/s |
| Capacity | Up to 22TB | Up to 8TB |
| Cost | $60 for 2TB | $90 for 2TB |
| Component Design | Mechanical | Solid-State |
| Durability and Reliability | Prone to physical damage | Highly durable |
What is a Solid State Drive (SSD)?
An SSD, or solid-state drive, is a new kind of storage that uses NAND flash memory and has no moving parts. This makes it faster, more durable, and more efficient than traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs).
How SSDs Work
SSDs use NAND flash memory to store data, even when turned off. The SSD controller is critical; it spreads data, manages wear and tear, and uses the TRIM command for better performance. Without moving parts, SSDs are just a board with flash memory chips, offering quick read and write times.
Advantages of SSDs
SSDs have many benefits:
- Speed: They can read and write data up to 500 MB/s, much faster than HDDs. Random access is also much quicker, making them ideal for fast data handling.
- Durability: With no moving parts, SSDs are less likely to break. They’re also more resistant to physical damage and environmental changes.
- Power Efficiency: SSDs use less power than HDDs. They draw between 0.1 to 0.6 watts when idle and up to 4.0 watts at peak, making them more energy-efficient.
| Aspect | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Sequential Read/Write Speed | 300 – 500 MB/s | 100 – 160 MB/s |
| Random Read/Write Speed (IOPS) | 20,000 – 100,000 | 75 – 100 |
| Idle Power Draw | 0.1 – 0.6 W | 4.0 – 6.0 W |
| Maximum Power Draw | 2.0 – 4.0 W | 6.5 – 9.0 W |
SSDs are a game-changer in computing, offering speed, reliability, and efficiency. They’re the go-to choice for anyone looking for the best in storage drive technology.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Efficiency
SSDs and HDDs have key differences in speed and energy use. These differences affect how well they perform in storage tasks.
Read and Write Speeds
SSDs and HDDs differ a lot in how fast they read and write data. A 7200 RPM HDD can go from 80-160 MBps. But, a SATA SSD can go from 200 MBps to 550 MBps.
For NVMe M.2 SSDs, the speed goes way up, over 5000 MBps. This means SSDs are about five times faster than HDDs. They’re great for tasks that need quick data access and transfer.
“Show the difference in speed between SSD and HDD using two vehicles, one sleek and fast, the other bulky and slow, racing towards the finish line.”
Even high-performance HDDs can’t beat modern PCIe NVMe SSDs. For example, the Crucial T700 SSD has 11,700/9500 MBps speeds. This shows how much faster SSDs are.
Energy Consumption
SSDs use less power than HDDs because they don’t have moving parts. This means they use less energy and make less heat. This is good for laptops because it helps with battery life and keeps the device cooler.
HDDs, with their moving parts, use more power and make more heat. So, SSDs are better for mobile devices and places where power is a concern.
In summary, SSDs are better for speed and saving energy. They’re faster and use less power, making them great for everyday and professional needs. They offer faster data transfer rates and reliable performance.
Durability and Reliability of SSDs and HDDs
Choosing between SSDs and HDDs means understanding their durability and reliability. These storage drives have their own strengths and weaknesses. They depend on their design and technology.
Mechanical Vulnerability of HDDs
HDDs are often questioned for their reliability because of their mechanical parts. Spinning platters and moving read/write heads can break from drops, shocks, or vibrations. This makes HDDs less reliable over time.
Longevity of SSDs
SSDs, on the other hand, are known for their durability. They don’t have moving parts, so they’re less likely to get damaged by physical harm or extreme conditions. They use wear levelling technology to spread data evenly, keeping them working well for a long time. The life of an SSD depends on the type of NAND flash it uses. For example, SLC SSDs can handle about 100,000 P/E cycles, while QLC SSDs are made for around 500 P/E cycles.
Data Recovery Considerations
Regarding data recovery, HDDs are often more accessible because of their mechanical design. Experts can recover data even if part of the drive is damaged. SSDs, though durable, are more challenging to recover data from because of how they store data electronically. SSDs may not show signs of failure until they suddenly stop working, but they are reliable.
| Comparison Factor | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High (No moving parts) | Moderate (Mechanical parts) |
| Drive Lifespan | Varies (Dependent on wear leveling and NAND type) | Moderate (Dependent on mechanical integrity) |
| Mechanical Vulnerability | Low | High |
| Data Recovery | Complex | Generally easier |
| Average MTBF | 1.5 million hours | 300,000 hours |
The table shows the main factors affecting SSD and HDD durability and reliability. Each drive type meets different needs, from rugged, shock-resistant storage to large, affordable storage solutions. Knowing these details helps you choose the right storage drive for your needs.
Storage Capacity and Cost Analysis
Looking at storage capacity and cost is critical. We must consider the cost per GB and the storage options for SSDs and HDDs. SSDs are usually pricier, but the cost difference between them and HDDs is getting smaller. Knowing this helps us make intelligent choices about storage.
Per GB Cost
The cost per GB helps us compare storage solutions. SSDs use NAND flash memory and are pricier per GB than HDDs with magnetic storage. But SSD prices are dropping. HDDs are still a good deal, offering more storage for less money. For example, a 500 GB HDD can cost less than USD 40.
Available Storage Options
SSDs and HDDs come in various capacities for different needs. SSDs range from 128 GB to 2 TB, with some top models up to 30.72 TB or 100 TB. Their falling prices make them more appealing for those needing fast access and reliability. However, HDDs go up to 20 TB for business use and are known for being affordable. HDDs offer from 250 GB to several terabytes for everyday users, meeting many storage needs. The comparison shows SSDs are getting cheaper, but HDDs are still the best deal for lots of storage.
“HDDs remain the most affordable storage type, with prices decreasing as storage capacity increases. An SSD’s lower per GB cost offers better speed and durability but might not be as cost-effective as larger HDD options.”
- Consider per GB cost when budgeting for storage.
- Evaluate storage needs to decide between SSD and HDD options.
In conclusion, picking the proper storage means balancing the cost per GB and how much storage you need. Users can find the best performance, price, and usefulness mix by understanding these factors.
SSD vs HDD: Which is Right for You?
Choosing between an SSD and an HDD depends on your storage and performance needs. Knowing what you need can improve your computing and save money when upgrading.
Use Case Scenarios
How you use your computer affects your choice between SSD and HDD. If you need fast boot times and quick access to files, go for SSDs. They use flash memory for speed and responsiveness. Gamers and professionals find SSDs cut down on loading times and stuttering.
For those needing lots of storage, HDDs are a better deal. They’re great for storing a lot of data without the high speed of SSDs. Many people use an SSD for the OS and apps and an HDD for big files and backups.
Budget Considerations
Your budget is critical in this choice. HDDs have been cheaper, offering more storage for the price. Western Digital has HDDs up to 28TB, which is perfect for storing much data.
SSDs are getting cheaper, too, making them suitable for those who want speed over storage. They use less energy and last longer because they have no moving parts. This means they can save you money over time. When deciding, consider your budget and what you need from your computer.
It’s all about balancing your current needs and plans. Both SSDs and HDDs have their perks. Knowing what you need can help you make an intelligent choice.
The Future of Data Storage: Evolution of SSD and HDD Technologies
The future of storage looks bright as SSD and HDD technologies improve. With innovations, these storage solutions are ready to handle our growing need for more efficiency and capacity.
Innovations in SSD Technology
SSD innovations are leading the way in storage technology. The industry is changing fast with the rise of NVMe protocols and drives like Intel’s 32TB P4500. SSDs come in many sizes, from small for mobile devices to big for data centres. They’re moving away from the old 2.5-inch design to fit directly into system boards, making them faster and more efficient.
Significant steps in SSD tech include the 100TB SSD from Nimbus Data. Switching to NVMe interfaces has made SSDs much faster than SATA ones. This means SSDs are now up to a hundred times quicker, giving you almost instant data access and boosting system speed.
Potential Improvements in HDDs
Even as SSDs grow in popularity, HDDs are still vital in the future of storage. Since 1956, HDDs have been a mainstay, thanks to innovations like helium in drives and technologies like MAMR and HAMR. These advancements have increased storage capacity and efficiency. Now, HDDs can hold up to 10 terabytes, making them a budget-friendly choice for storing lots of data.
HDDs have seen a massive drop in cost per gigabyte over the years. They can now be as cheap as three cents per gigabyte, appealing to those who need lots of storage without focusing on speed. These updates keep HDDs competitive and valuable in the data storage market.
The future of data storage will blend SSD and HDD technologies. As they improve, we’ll see storage solutions that meet different needs. This will range from fast laptops to massive data centres.
| Feature | SSDs | HDDs |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Capacity | Up to 100TB | Up to 10TB |
| Cost per GB | Higher | As low as $0.03 |
| Speed | Up to 64,000MB/s | Much slower |
| Form Factors | Various (2.5″, mSATA, M.2) | Primarily 3.5″ and 2.5″ |
| Reliability | Higher (No moving parts) | Lower (Mechanical parts can fail) |
Impact of Storage Type on System Performance
The type of storage in a computer significantly affects its speed and efficiency. This includes how fast it boots up, loads apps, and performs tasks. The difference between SSDs and HDDs is enormous for those who value speed.
Boot Times
SSDs make computers start up much faster than HDDs. You can expect to wait about 10-13 seconds for an SSD to boot, compared to 30-40 seconds for an HDD. This is because SSDs can read and write data much quicker, up to 7,000 MB/s, while HDDs usually do it at 500 MB/s.
Application Load Times
SSDs don’t just speed up boot times; they also make apps load and run faster. Loading an app from an SSD can be 20 times quicker than an HDD. HDDs move data at 30–150 MBps, while SSDs can move it at 500–3,500 MBps. This means tasks like video editing, gaming, and coding are done much quicker and more efficiently.
The table below shows how SSDs outperform HDDs in key areas:
| Metric | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Boot Times | 30-40 seconds | 10-13 seconds |
| Read/Write Speed | Up to 500 MB/s | Up to 7,000 MB/s |
| File Transfer Speed | 30–150 MBps | 500–3,500 MBps |
| Capacity (Top-End Consumer) | 20 TB | 8 TB |
| Cost (per GB) | $0.03–0.06 | $0.08–0.10 |
While HDDs might be cheaper for more storage, SSDs offer better performance. They provide faster boot times and quicker app loading. For those who need speed and efficiency, SSDs are the better choice.
Common Misconceptions and Myths about SSDs and HDDs
Many users have SSD myths and HDD misconceptions. It’s key to clear up these storage device myths for better choices. Here, I’ll share the facts about SSDs and HDDs.
Another myth is that HDDs are outdated because they’re slow. While SSDs are faster, HDDs still offer much storage for less money. For example, the Mozaic 3+ platform aims for over 3TB per platter and maybe 5TB, making them a smart choice for storing lots of data.
Some believe SSDs are too expensive. But, SSD prices are dropping, and SATA-connected SSDs are now about half the price of SAS HDDs per terabyte. NVMe drives are also getting cheaper, making SSDs and HDDs closer in price.
Defragmenting SSDs helps them work better. However, defragmenting can slow down an SSD and shorten its life. Modern SSDs handle data well, using the TRIM command to keep up performance and last longer.
| Storage Type | Capacity | Performance | Cost-per-TB | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Drives (HDDs) | 16TB max | Slower | Lower | High |
| Solid State Drives (SSDs) | 32TB and rising | Faster | Higher | Very High |
By debunking storage myths and sharing drive technology truths, you can now decide if SSDs or HDDs are right for you. Consider their capacity, speed, cost, and reliability.
Conclusion
In this SSD vs HDD comparison, we examined the main differences between SSDs and HDDs. We aim to help you make an intelligent storage choice. Each storage type has its benefits, so the best option depends on what you need and want.
SSDs are known for their fast speed, low energy use, and reliability. They give you quick access to your data, making your computer start up faster and run smoother. They also produce little heat, are quieter, and are much less likely to break than HDDs.
However, HDDs are a good deal for those who need lots of storage space but don’t want to spend a lot. They’re cheaper per gigabyte, making them great for storing many files or extensive programs. SSDs are slower than they are, but they’re still a good choice for many people because they’re affordable and easy to find.
So, choosing SSD or HDD depends on what you need and how you use your computer. If you want speed, reliability, and top performance, go for SSDs. But HDDs might be the better option if you’re watching your budget and need lots of storage. Knowing these differences helps you pick the best storage for your needs.
FAQ
What is the difference between SSD and HDD?
The primary difference between SSD and HDD lies in how they store data. A solid-state drive (SSD) uses flash memory to read and write data, making it much faster and more durable than a hard disk drive (HDD), which relies on a spinning disk and moving parts like an actuator arm to access data.
How do SSDs outperform HDDs in terms of speed?
SSDs are faster than HDDs because they use flash memory rather than mechanical parts. This means they have quicker load times, faster data transfer rates, and better performance when handling large files. An NVMe SSD can offer even greater speeds compared to traditional SATA SSDs.
Which is more durable, SSD or HDD?
In terms of durability, SSDs have a clear advantage over HDDs. Since SSDs have no moving parts, they are less prone to physical damage from drops or bumps. With their spinning disks and actuator arms, HDDs are more susceptible to mechanical failure.
What about storage capacities between SSD and HDD?
HDDs generally offer more storage space at a lower cost compared to SSDs. While SSDs are catching up, larger storage capacities are still more affordable with HDDs. However, for many




